Latest Advancements in US Navy Drones
5. RQ-21A Blackjack

The RQ-21 Blackjack small tactical unmanned air system (STUAS), previously known as the Integrator, has been designed and built by Boeing company Insitu for the US Navy’s STUAS programme.
The 36.7kg UAV features six payload areas, which can hold a maximum payload of 17kg. The electro-optic/infrared (EO/IR) payloads aboard the aircraft enable the operators to conduct intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), battle damage assessment, communications relay, search-and-rescue, force protection, border security, and anti-piracy missions.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
The RQ-21 Blackjack offers a line of sight (LoS) range of 102km. Powered by an 8HP reciprocating engine, the unmanned aircraft can reach a maximum altitude of 20,000ft. The maximum speed and endurance of the UAV are 167km/h and 16 hours respectively.
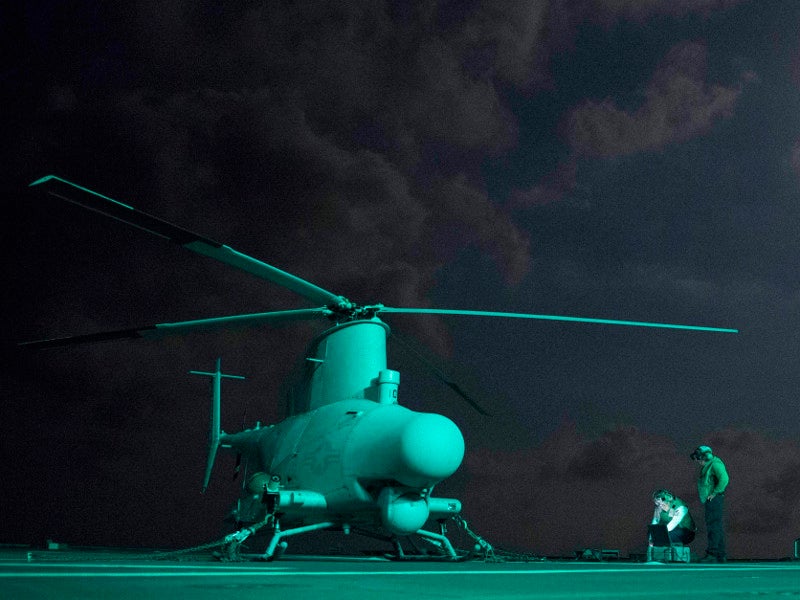
4. MQ-8B Fire Scout

The MQ-8B Fire Scout autonomous unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) has been in service with the US Navy since 2009. Developed by Northrop Grumman Systems Corporation, the vertical take-off and landing tactical unmanned aerial vehicle (VTUAV) is based on Schweizer aircraft model 330.
Powered by a single Rolls Royce 250-C20W heavy fuel turbo-shaft engine, the VTUAV is capable of carrying payloads weighing 136kg. It is capable of flying for more than seven hours with a baseline payload and covers a range up to 1,103km. The autonomous aircraft can reach a speed up to 85k and has an altitude ceiling limit of 12,500ft.
The MQ-8B’s autonomous nature, longer endurance and greater payload carrying capacity enable it to identify, track and notify targets, as well as provide targeting data, carry out ISR and perform battle damage assessments. The payload includes EO/IR sensors with laser range finder (LRF), mine detector, maritime radar, and communication relay.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData3. MQ-8C Fire Scout

The MQ-8C Fire Scout fully autonomous unmanned aircraft was built based on the MQ-8B platform. The advanced VTUAV variant made its first flight in November 2013 and was delivered to the US Navy in December 2014. Developed by Northrop Grumman, the next-generation VTUAV also shares the capabilities of Bell 407 helicopter.
The MQ-8C possesses greater abilities than its predecessor MQ-8B. The MQ-8C’s range doubles to 2,272km, while its endurance is up to 12 hours. Its maximum speed is 135k and the service ceiling is 16,000ft. The UAV has a payload carrying capacity of 226kg and can additionally convey external sling loads up to 1,202kg.
The bigger MQ-8C is powered by Rolls-Royce 250-C47E engine equipped with a full authority digital electronic control (FADEC) system. It carries a coastal battlefield reconnaissance and analysis (COBRA) mine detector apart from the payloads carried by MQ-8C. The autonomous aircraft can further be configured to transport other payload varieties.
2. X-47B UCAV

The X-47B is a fighter-sized unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) developed by Northrop Grumman, as part of the US Navy carrier demonstration (UCAS-D) programme. It is a naval version of the X-47A Pegasus technology demonstrator aircraft.
The first X-47B demonstrator aircraft made its first flight in February 2011, while the first catapult launch was conducted in November 2012. The first UCAV is expected to enter service with the US Navy in 2020. Equipped with EO/IR payloads, the aircraft can support aerial refuelling, surveillance, reconnaissance, intelligence and strike missions.
The X-47B is the first unmanned aircraft to perform autonomous launch and recovery aboard an aircraft carrier and the first to conduct in-flight refuelling. It has a wingspan of 18.9m, maximum gross take-off weight of 19.95t, and payload capacity of 2,000kg. Powered by a Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-220U engine, the UCAV can fly at high subsonic speeds and attain a maximum range of 2,100nmi (3,889km). It has an endurance of 14 hours and a maximum operational altitude of 40,000ft.
1. MQ-4C Triton

The MQ-4C Triton is a high-altitude, long-endurance (HALE) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) developed by Northrop Grumman for the US Navy. It is a derivative of the US Air Force’ RQ-4B Global Hawk.
The UAV entered service the US Navy’s service in May 2018, after five years of its first flight. It can support persistent maritime ISR, signals intelligence, search-and-rescue, and communications relay missions. The primary payload of the unmanned aircraft is the AN/ZPY-3 multi-function active-sensor radar.
The MQ-4C Triton has a maximum gross take-off weight of 14,628kg and can respectively carry maximum internal and external payloads of 1,452kg and 1,089kg. Powered by a Rolls-Royce AE3007H turbofan engine, the MQ-4C Triton can fly non-stop for 24 hours at altitudes up to 56,500ft. It has a maximum speed of 592km/h and an operational range of 15,186km.