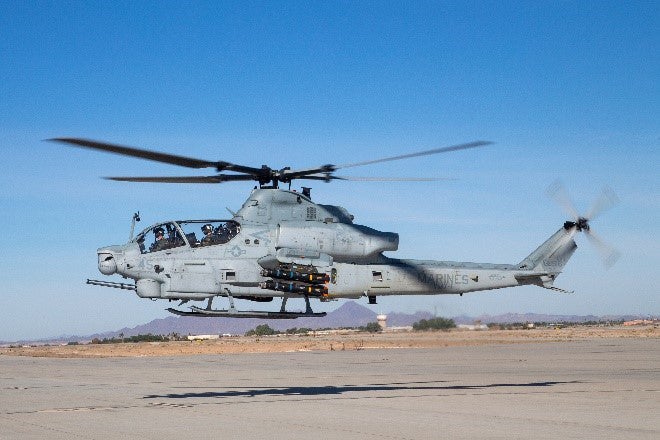
The US Marine Corps’ (USMC) AGM-179A Joint Air-to-Ground Missile (JAGM) has achieved initial operating capability (IOC) for use on the AH-1Z Viper helicopter.
The missile successfully completed an extensive initial operational test and evaluation period.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
In November last year, it was test fired from AH-1Z off the coast of Florida and in the following month, it was put through land-based testing in Arizona.
The tests helped to determine the effectiveness and suitability of JAGM to support expeditionary advanced base operations, including close air support missions and conducting strikes.
US Naval Air Systems Command precision-guided missiles deputy programme manager commander Reid Adams said: “IOC marks a major milestone for the JAGM programme and significant increase in capability for the AH-1Z.
“This accomplishment is a true testament of the tireless efforts made by so many across DoD and our industry partners to support the war fighter.”

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataJointly developed by the US Navy and the US Army, JAGM has already achieved IOC on the US Army’s AH-64E Apache helicopter.
JAGM is a precision-guided missile and its design blends two sensor technologies, a semi-active laser (SAL) system and millimetre wave radar (MMW).
It is designed to target high-value, stationary and moving, land and maritime threats day or night in adverse weather, battlefield obscured conditions and against different countermeasures.
A multi-purpose warhead, JAGM, is used on fixed-wing, rotary-wing, uncrewed aircraft system platforms.
USMC H-1 light, attack helicopter programme manager colonel Vasilios Pappas said: “Incorporating systems such as JAGM on the AH-1Z is essential in keeping the platform at the forefront of warfighting capabilities.”