BAE Systems secures contract from Boeing to improve the US Navy's MQ-25A unmanned aerial refueler, boosting computing power and paving the way for capabilities and reduced operational costs.
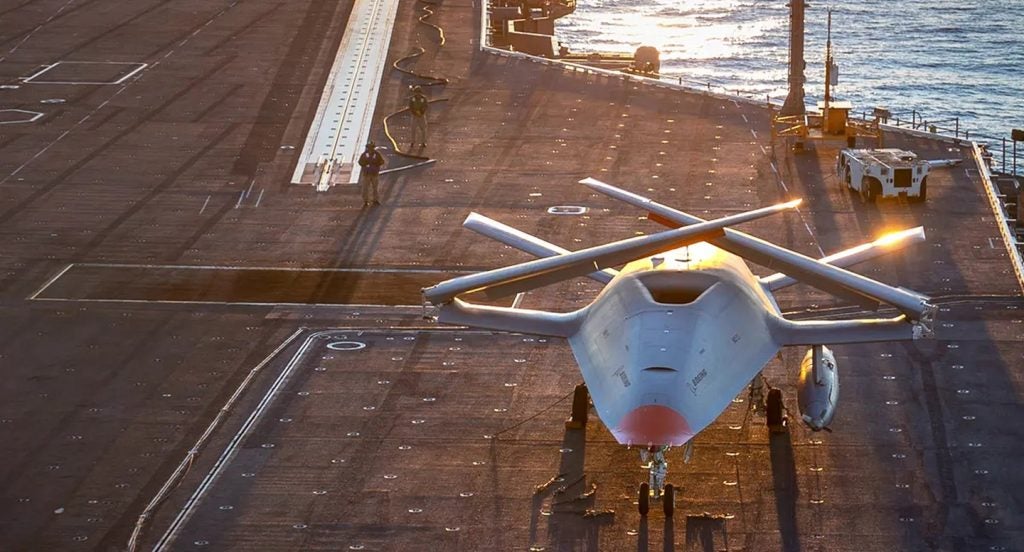
In a move set to change the unmanned aerial refueler, BAE Systems has been entrusted with upgrading the vehicle management system computer (VMSC) for the US Navy's MQ-25 unmanned aerial refuelling system. This technological advancement, announced in collaboration with Boeing, aims to improve the MQ-25's capabilities while addressing obsolescence concerns.
The next-generation VMSC, developed by BAE Systems, is poised to serve as the nerve centre of the MQ-25, controlling all flight surfaces and overseeing vehicle management duties for the autonomous aircraft. As the Navy's carrier-based unmanned aircraft, the MQ-25 plays a role in augmenting aerial refuelling capabilities while alleviating the workload of F/A-18 aircraft, bolstering the fleet's operational capacity.
The US Navy has plans to procure up to two squadrons of MQ-25A Stingray UAVs to reduce its dependency on manned aircraft tankers. Boeing will capture a 27% share of the military UAV market in North America with a forecast revenue of $7.7bn over the 2022–32 period, according to GlobalData's intelligence on the global military unmanned aerial vehicles market.
Corin Beck, senior director of military aircraft systems for controls and avionics solutions at BAE Systems, emphasised the potential of the upgraded VMSC, stating, "Our upgraded VMSC for the MQ-25 will deliver advanced functionality—enabling this platform to execute today and tomorrow's critical missions, while also reducing the amount of hardware required on the aircraft through consolidation into this computer."
Valued at $805.3m and awarded in August 2018, the US awarded Boeing a contract to design, develop, and supply four MQ-25A Stingray refuelling aircraft. These UAVs are poised to enhance the carrier air wing's performance, efficiency, and safety, extending the range of deployed aircraft such as the F/A-18 Super Hornet and F-35C.
This VMSC upgrade, characterised by quad-core processors, enhances computing power and optimises size, weight, and power footprint on the MQ-25 aircraft.
By replacing multiple onboard computers with an integrated system, the upgraded VMSC enhances aircraft reliability while reducing the total lifecycle cost of ownership for the Navy. Moreover, the new VMSC lays the groundwork for future missions of the MQ-25, including intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) operations, while pioneering the concept of manned-unmanned teaming (MUM-T) for all carrier-based unmanned systems.
The upgrade is being conducted at BAE Systems' engineering and manufacturing facility in Endicott, New York.
In addition to the VMSC upgrade, BAE Systems also provides the Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) System for the MQ-25 aircraft.