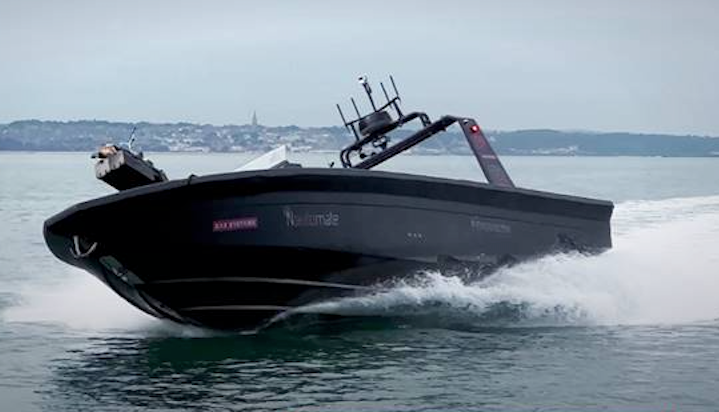
BAE have shown the first use of Nautomate, an autonomy solution allowing for the conversion of customer vessels to run as an uncrewed platform for the first time at the Defence and Security Equipment International (DSEI) 2023 on 13 September. The collaboration with UES introduced the system to a speedboat, allowing the vessel to run at high speed for durations normally incompatible with having a living crew aboard.
While BAE have a long history with autonomous systems, this is the first time the company has introduced autonomous function to a platform made by another company.
“It's a new technology. It's got a whole lot of regulatory and assurance that's new to the world as well,” said Micahel Blake, BAE’s business development manager for the project.
Blake emphasised the advantage in taking “the man out of the loop” in terms of running the vessel at levels difficult to endure with a crew aboard, referencing the 4-hour shift time-limits for human crew to avoid vibration and shock threats. Requiring personnel to travelling at 20 knots for 24 hours in sea state 3 conditions, with waves up to 1.25m, would not be feasible, but it is a reasonable expectation for the uncrewed vessel BAE displayed at DSEI.
This kind of endurance has applications in a sensing role, outfitted with ISR systems, but the display vessel was also outfitted with an anti-propeller net weapon system for snaring and immobilising other ships.
BAE are not able to discuss potential future Nautomate partners, but have been involved in a number of earlier activities testing autonomy, including the use of autonomous systems in live fire trials on ranges under the umbrella of the UK Royal Navy, and trialled an uncrewed autonomous Pacific 24 Rigid Inflatable Boat for the Royal Navy in 2020.
The Nautomate system has a scalable architecture that makes it suitable for platforms from 6m to 50m in overall length, either as an upgrade to an existing vessel or integrated during production.