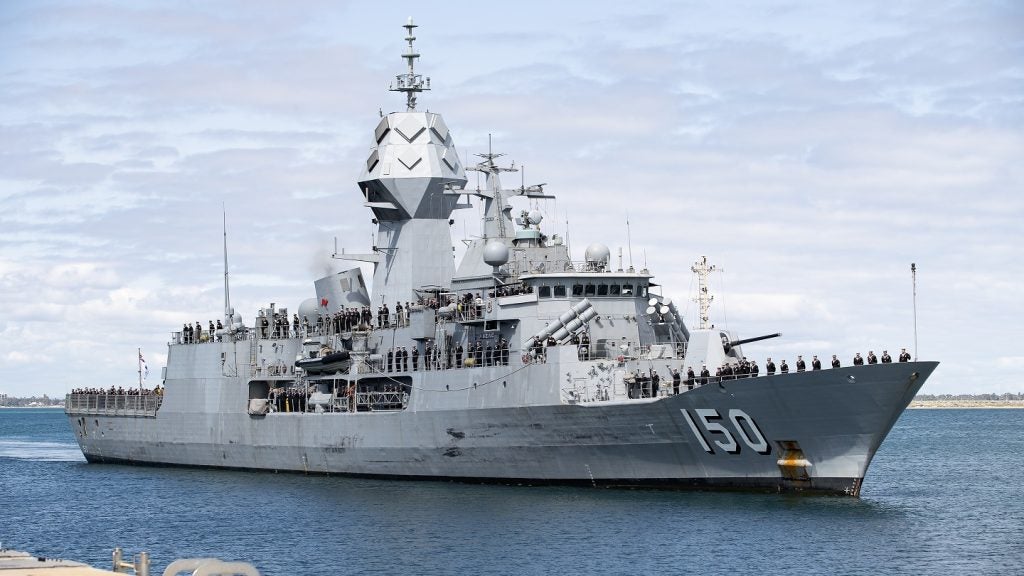
The long-serving eponymous lead vessel of the Anzac-class guided missile frigates (FFG) of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) has been decommissioned after 28 years in operation in what might be seen as the first major step in a wider restructuring of the RAN surface fleet.
Decommissioning HMAS Anzac will pave the way for the long-term investment in enlarging and enhancing the RAN’s fleet, in response to the recommendations made by the Independent Analysis of Navy’s Surface Combatant Fleet, stated the Australian Department of Defence, in an 18 May 2024, release.
With the announcement, it was confirmed that HMAS Anzac would be the first of the Anzac-class FFGs to be retired, followed by its sister ship HMAS Arunta in 2026. With the decommissioning of HMAS Anzac, the RAN has seven vessels of the class still in service.
If each of the remaining Anzac’s is expected to service for around 28 years, the last vessel in class, HMAS Perth, could be decommissioned in the 2034 timeframe.
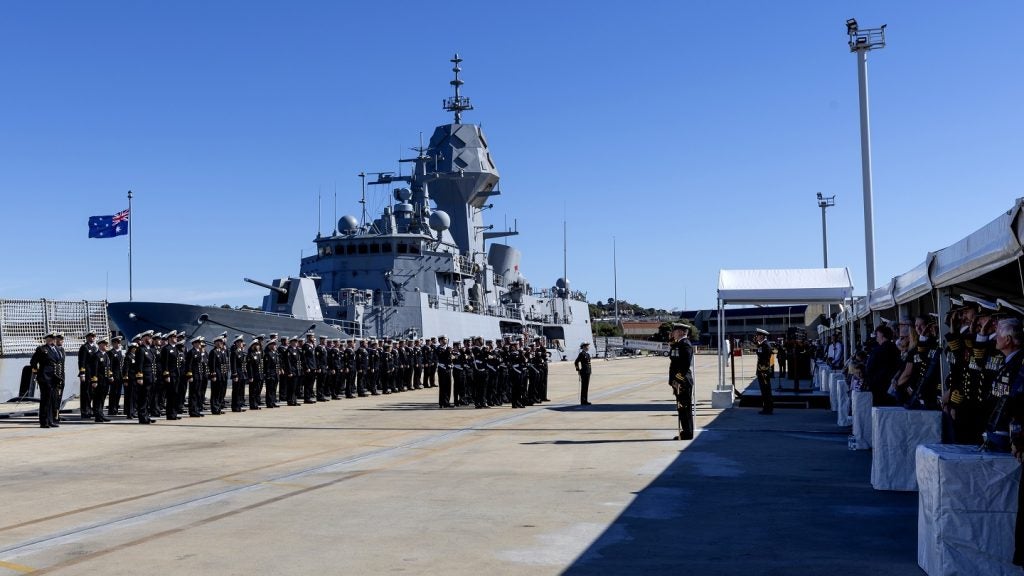

In February, the Australian Government announced that it would scrap the planned upgrades to the Anzac class, which are to be replaced by 11 new general-purpose warships able to conduct land and maritime strike, air defence, and maritime security operations.
The acquisition of the new general-purpose frigate was to be accelerated to replace the Anzac-class frigates, meaning the ‘Transition Capability Assurance’ upgrades would no longer be required. The new general-purpose frigates will require smaller crews than the Anzac class, the Australian Government stated.
With the decommissioning of HMAS Anzac, the RAN’s main surface combatant fleet has been reduced to ten frigates and destroyers, the latter type being the Hobart-class guided missile destroyers. Under the restructure of the RAN, the Hobart class will be upgraded with Aegis air defence capabilities.
The restructure also saw the reduction of the UK Type 26-derived Hunter-class frigate acquisition from nine hulls down to six, with the first vessels not expecting to enter service until 2031 at the earliest, potentially running into 2032.
Under original planning, the upgraded Anzac class was expected to begin decommissioning after 2030, and potentially into the 2040s.
Anzac-class frigates: Australia’s naval workhorse
In November 1989, the joint Australian/New Zealand frigate project contracted Australian shipbuilders Tenix Defence Systems (now BAE Systems Australia) to construct ten Anzac-class frigates; eight for Australia and two for New Zealand. The first frigate, HMAS Anzac, was commissioned for the RAN in May 1996.
The 3,600 tonne frigates were built at Tenix’s Williamstown yard in Victoria, Australia. The design is based on the Blohm + Voss Meko 200 modular platform which utilises a basic hull and construction concept to provide flexibility in the choice of command and control, weapons, equipment and sensors, depending on national requirements.
The RAN’s Anzac class have been extensively upgraded over their lifetime, adding new anti-submarine and anti-surface weapons capabilities, as well as updated radars. However, the cancellation of the Transition Capability Assurance programme, which would have extended their service life by several years, has brought an end to their upgrade process with the vessels now expected to operate with what capabilities they have until decommissioning.
In cancelling the Transition Capability Assurance programme, the RAN has sought to save the more than A$600m ($401m) assigned for the Anzac upgrade, which was also known as Sea 5014 Phase 1.
Additional reporting from John Hill.