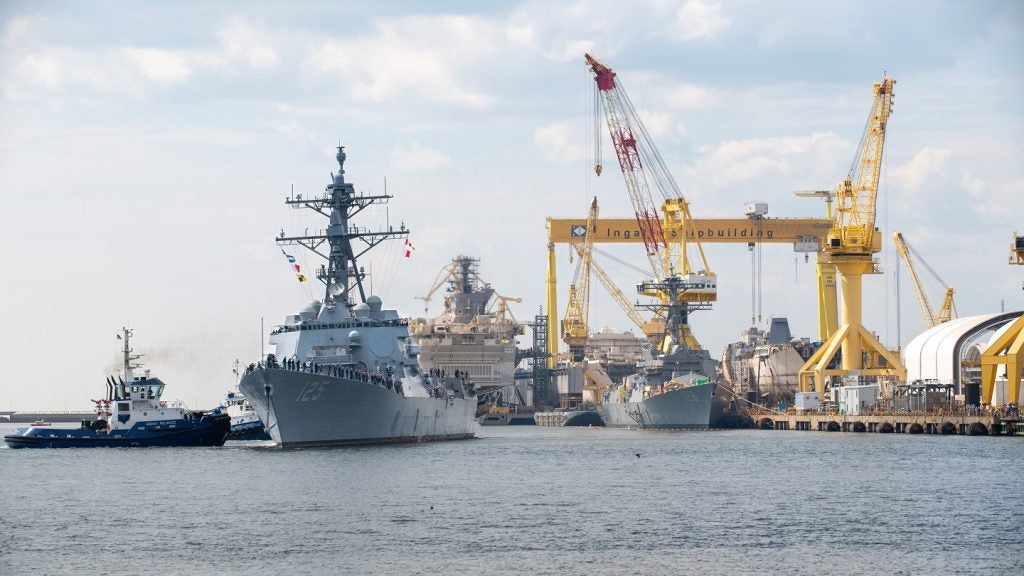
The first of the Flight III Arleigh Burke-class guided missile destroyers, USS Jack H Lucas (DDG 125), is nearing its entry into US Navy service following its departure from Ingalls Shipbuilding site in Pascagoula on 26 September.
According to a release from HII, the USS Jack H Lucas will be commissioned on 7 October at a ceremony in Tampa, Florida, on the US eastern seaboard before sailing to its homeport of San Diego on the west coast.
The commissioning of a warship is the final step in a complex process to determine whether the vessel is able to perform its operations as originally planned. The 26 September ‘sail away’ of the USS Jack H Lucas from the HII site is the final official step before it can be commissioned into service.
However, on 22 September the US Department of Defense (DoD) awarded a $20m modification to a previously awarded contract to BAE Systems San Diego Ship Repair for the accomplishment of a post-shakedown availability (PSA) process, as well as procurement of additional materials in support of the PSA.
The PSA contract modification, as stated by the DoD, was for “one Arleigh Burke class guided missile destroyer (DDG 125)”.
Work on the PSA contract modification for DDG 125 is expected to be completed by October 2024, a full year after the vessel is scheduled to be commissioned into USN service.
According to the Navy League of the United States, a civilian non-profit, a PSA is “an industrial activity availability assigned to correct deficiencies found during the shakedown cruise or to accomplish other authorised improvements”.
This definition is also used by the Federation of American Scientists, which in its guide on US Navy PSA doctrine, states that a PSA deficiency correction period will be “scheduled after Sea Trails and prior to PSA completion”, with the scheduled length of the correction period “determined by the type and magnitude of the remaining deficiencies”.
US Navy Flight III DDGs
The Arleigh Burke-class DDG series first entered service with the US Navy in 1991, and has since been upgraded to the Flight II, Flight IIA, and now Flight III iterations.
According to the US Navy, DDGs 51-71 represent the original design and are designated as Flight I; DDGs 72-78 are Flight II ships; and DDGs 79-124 and DDG 127 are Flight IIA ships. The Flight III baseline begins with DDGs 125-126 and continues with DDG 128 and subsequent vessels.
Replacing the legacy Charles F. Adams class (DDG 2), the DDG 51 series was designed with an all-new hull form, incorporating much of the Spruance class (DD 963) propulsion and machinery plant, and the integrated Aegis Weapons System (AWS) from the Kidd-class (DD 993) destroyers and installed on the larger, and still in service, Ticonderoga-class cruisers.
The Flight III vessels have been designed to be able to accommodate future energy-based weapons systems and sensors and will form the backbone of the US Navy’s surface-based ballistic missile detection capability.
The AWS is composed of a multi-function phased array radar, anti-air warfare (AAW) and anti-submarine warfare (ASW) systems, vertical launch missiles, and the Tomahawk cruise missile weapon system. The latest Flight III, with the AMDR, enables the class to simultaneously perform AAW and ballistic missile defence capabilities.
HII states that it has delivered 35 Arleigh Burke-class destroyers to the US Navy over the lifetime of the programme, including the Jack H Lucas (DDG 125), in June 2023. The company has four other Flight III destroyers currently under construction including Ted Stevens (DDG 128), Jeremiah Denton (DDG 129), George M Neal (DDG 131) and Sam Nunn (DDG 133).
DDG 125 includes the AN/SPY-6(V)1 Air and Missile Defense Radar (AMDR) and the Aegis Baseline 10 Combat System.
In August, the US DoD secured contracts for the construction of ten new flight III Arleigh Burke-class (DDG 51) destroyers. The timeframe for the vessels will see HII’s shipbuilding division construct seven destroyers – two in 2023, one in 2024, two in 2025, one in 2026, and one in 2027.
Within the same period General Dynamics Bath Iron Works (BIW) will also build three units – one ship per fiscal year in 2023, 2024, and 2026.
Additional reporting by John Hill.