Icon-PEP enables deployment of IP Applications over an HF network using STANAG 5066 link layer as the interface to that network.
Icon-PEP provides two core services:
- Generic switching of IP packets over an HF network, causing it to act as an IP subnet. This enables support of any IP applications.
- Optimized support for TCP over IP using a Performance Enhancing Proxy (PEP) to optimize TCP performance over HF.
This enables a wide range of applications, such as Web browsing, to operate over HF. While in principle any application can be run, the choice of application in practice is constrained by the limited bandwidth and high latency of HF communication.
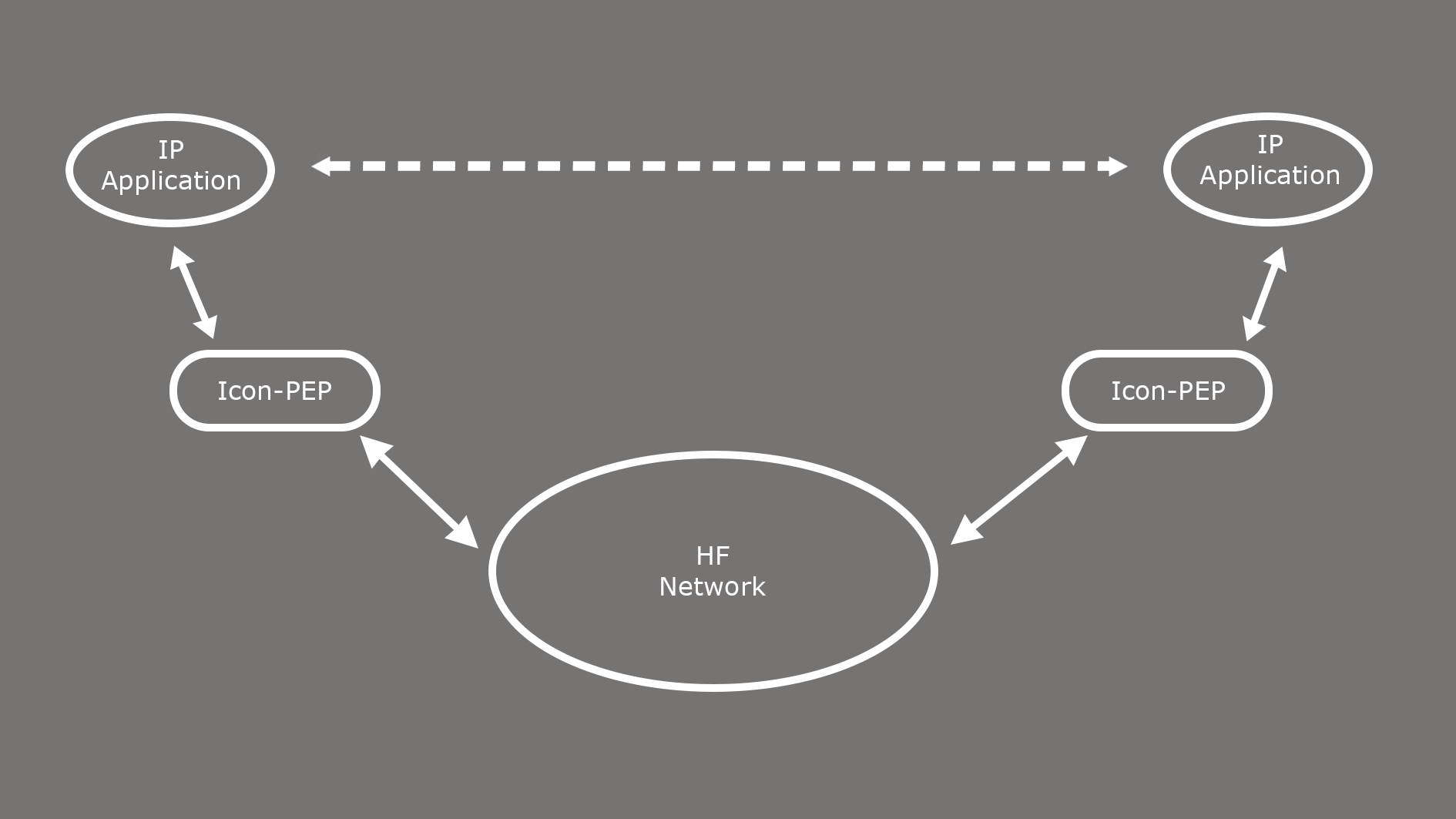
Deployment Model
The basic deployment model is shown below, a pair of IP applications (e.g., a Web client and a Web server) are separated by HF. At a very high level, Icon-PEP is enabling this communication. The diagram omits components between IP Application/Icon-PEP and between Icon-PEP/HF Network.
The communication between a pair of IP applications proceeds over a sequence of IP subnets, each one connected by a router. Icon-PEP enables an IP subnet to be created over HF, which forms one step in the complete IP communications setup.
Icon-PEP operates over the STANAG 5066 HF Link layer, and connects to a STANAG 5066 server such as Isode’s Icon-5066 product using the STANAG 5066 SIS protocol. This cleanly decouples Icon-PEP from the STANAG 5066 link layer.
It is important to note that Icon-PEP connects to an IP router, and not directly to a host (end system) or to an application. This gives flexibility to support many applications and hosts with a single Icon-PEP server.
Icon-PEP communicates with one or more IP Routers using Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE), specified in RFC 2784. GRE provides a simple mechanism to exchange packets between routers over IP, often described as a “GRE Tunnel”. Icon-PEP terminates the GRE tunnel from a connected IP router. This means that there is no requirement for a peer system to use GRE.
GRE is widely supported by Edge routers, and it is anticipated that Icon-PEP will generally connect to the deployed router. For subnets or single hosts that do not deploy a router, or where the deployed router does not support GRE, it is possible to use a software router, such as the one provided on many Linux systems or a product such as pfSense running in a virtual machine.
IP Switching & PEP
Icon-PEP provides two services. The first is simply to switch IP packets. This follows STANAG 5066 Annex U “IP Client” services for operating an IP subnet over HF. It simply transfers the IP packet. Icon-PEP provides controls based in the IP protocol used and ports within the protocol (e.g., ICMP, UDP). Packets can be handled differently based on protocol, including blocking, and choosing between ARQ and non-ARQ transfer.
Operation using IP Client is described in detail in the Isode whitepaper [Measuring and Analysing STANAG 5066 IP Client]. This shows that IP Client works well for some services, such as ICMP Ping, but not for others including TCP. Icon-PEP supports IPv4 and IPv6 complying to STANAG 5066 Annex U.

